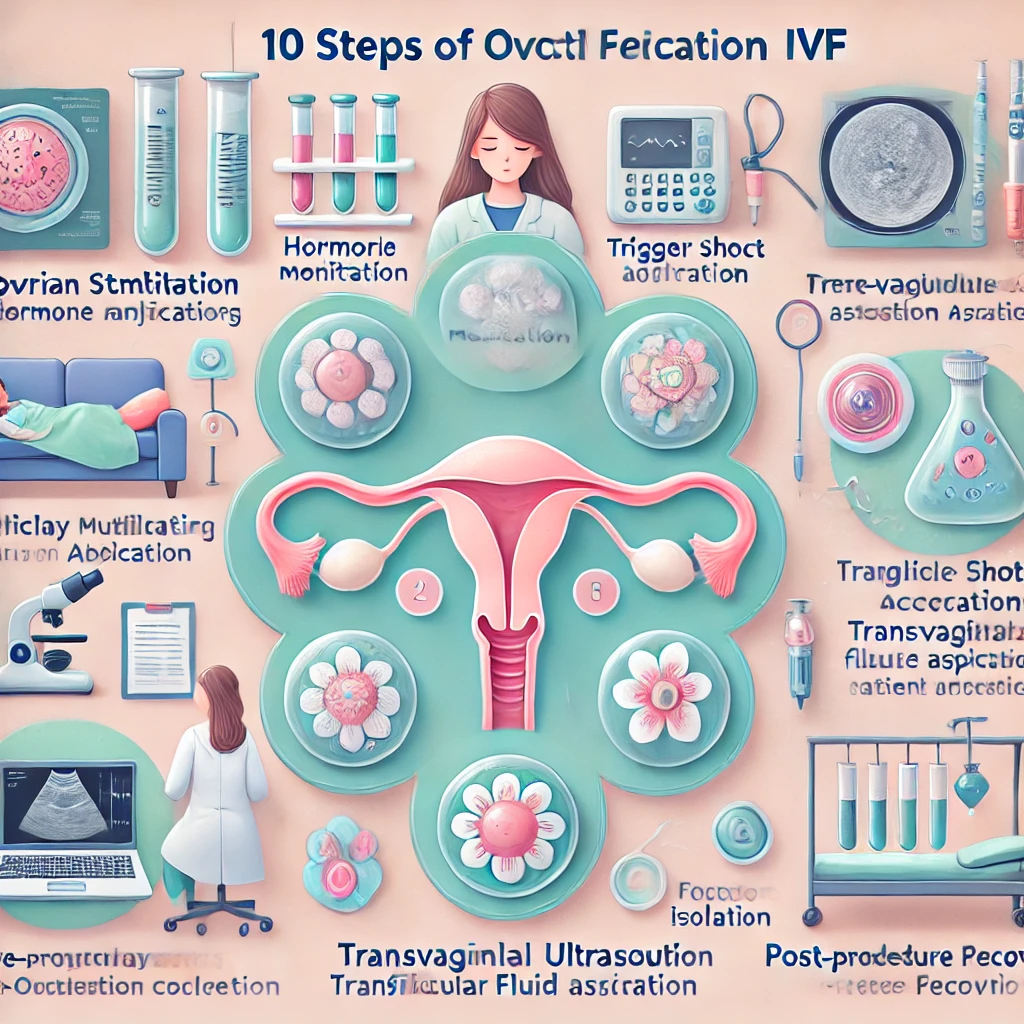
Oocyte retrieval, also known as egg retrieval, is a crucial step in in-vitro fertilization (IVF). This minimally invasive procedure involves extracting mature eggs from the ovaries to be fertilized in a laboratory. Below are the 10 key steps involved in oocyte retrieval:
1. Ovarian Stimulation
Before oocyte retrieval, the patient undergoes ovarian stimulation using hormone injections. These medications stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple follicles containing eggs, increasing the chances of retrieving mature oocytes.
2. Monitoring Follicle Development
Frequent ultrasounds and blood tests are performed to monitor the growth and development of follicles. Once the follicles reach the optimal size (18-20 mm), the patient is ready for the next step.
3. Triggering Ovulation
When the follicles are mature, a “trigger shot” of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) or a GnRH agonist is administered. This injection ensures the final maturation of the eggs and prepares them for retrieval. The retrieval is scheduled approximately 34-36 hours after the trigger shot.
4. Pre-Procedure Preparation
The patient is advised to avoid eating or drinking for 6-8 hours before the procedure. They are also asked to arrive at the clinic with a companion, as sedation is involved during the retrieval process.
5. Administration of Anesthesia
Oocyte retrieval is performed under mild sedation or local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. The anesthesia ensures the patient is comfortable and relaxed during the procedure.
6. Transvaginal Ultrasound Aspiration
Using a specialized ultrasound probe with a thin needle attached, the doctor carefully inserts the needle into the vaginal wall to reach the ovaries. This needle is guided into each follicle to aspirate the fluid containing the oocyte.
7. Collection of Follicular Fluid
The aspirated follicular fluid is immediately passed to the embryologist, who examines it under a microscope to identify the oocytes. Each follicle typically contains one egg, although some may not yield an oocyte.
8. Retrieval of Oocytes
The embryologist isolates the oocytes from the follicular fluid. The number of oocytes retrieved varies depending on the patient’s response to ovarian stimulation.
9. Post-Procedure Recovery
The patient is monitored in the recovery room for a short period after the procedure. Mild cramping or spotting is common, but these symptoms usually resolve within a day. The patient can typically return home within a few hours.
10. Laboratory Fertilization
The retrieved oocytes are prepared for fertilization. Depending on the fertility plan, the eggs may be fertilized with sperm through conventional IVF or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). Fertilized embryos are then cultured and evaluated for transfer or freezing.